Diabetes and Foot Health as you get older
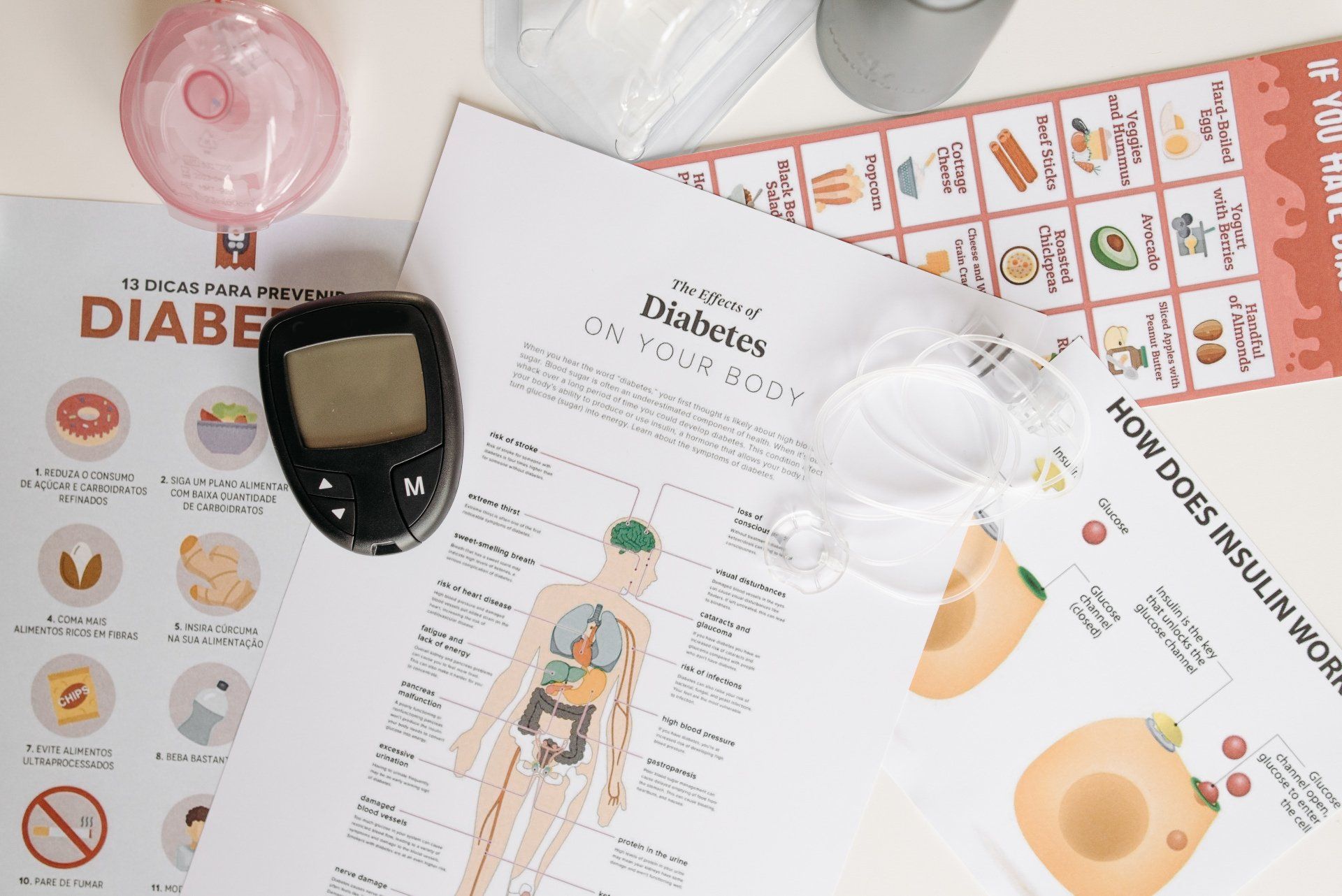
Diabetes and foot health become increasingly important as you get older, particularly because older individuals with diabetes are more susceptible to various foot-related complications. Diabetes can lead to nerve damage (neuropathy) and poor blood circulation, which can significantly impact the health of your feet. Here are some key considerations regarding diabetes and foot health as you age:
- Neuropathy Awareness: Neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes that affects the nerves, leading to reduced sensation in the feet. This makes it challenging to detect injuries, cuts, blisters, and other issues. Regularly inspect your feet for any abnormalities, even if you don't feel pain, and seek medical attention promptly for any concerning changes.
- Circulation Issues: Diabetes can impair blood flow to the extremities, including the feet. Reduced blood flow can delay wound healing and increase the risk of infections. It's important to maintain good blood glucose control and practice habits that promote circulation, such as staying active and avoiding smoking.
- Foot Ulcers and Wounds: Neuropathy and poor circulation can lead to the development of foot ulcers, which are slow-healing wounds. Foot ulcers can become infected if not managed properly and may lead to serious complications, including the need for amputation. Regular foot inspections and proper wound care are crucial.
- Proper Foot Care Routine: Establish and maintain a daily foot care routine. Wash your feet with mild soap and warm water, dry them thoroughly (especially between the toes), and apply a moisturiser to prevent dry skin. Avoid soaking your feet, as it can lead to overhydration and maceration of the skin.
- Trimming Nails Carefully: If you have neuropathy, be cautious when trimming your toenails. Trim them straight across and avoid cutting too close to the skin to prevent cuts and ingrown nails.
- Appropriate Footwear: Choose comfortable, well-fitting shoes that provide support and cushioning. Avoid wearing shoes that are too tight, as they can cause friction and pressure points. Always wear socks to prevent blisters.
- Avoiding Temperature Extremes: Neuropathy can affect your ability to sense temperature changes. Test the water temperature with your hand before immersing your feet in water. Avoid using heating pads or hot water bottles on your feet.
- Regular Medical Assessments: Include a thorough foot examination as part of your routine medical check-ups. A healthcare professional can assess the condition of your feet, identify any potential issues, and offer guidance on proper foot care.
- Avoiding Self-Treatment: If you notice any foot problems, such as blisters, cuts, redness, or swelling, avoid self-treatment. Consult a healthcare professional, preferably a podiatrist, for proper evaluation and treatment.
- Diabetes Management: Properly managing your diabetes by controlling blood glucose levels, monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of foot-related complications.
In summary, as you age with diabetes, paying attention to your foot health is essential to prevent complications and maintain overall well-being. Regular self-care, proper footwear, and routine medical assessments can help you minimise the risks associated with neuropathy and poor circulation, ensuring that your feet remain healthy and functional as you navigate the challenges of getting older with diabetes.
Book an appointment with a Foot Health Practitioner to assist you with your foot health.
